Equipment such as construction machinery, sound and lighting equipment, emergency medical defibrillators, and electrical power tools are often used in locations without a convenient power source, and extension cords are thus used to supply the current to the equipment. Read More…
Our customers find we have the highest standards when it comes to quality, and delivery. Quail Electronics is a worldwide power cord supplier, offering power cords and various other products.
All of our power cords are tested and stand up to rigorous demands of everyday application. We serve a global market including the United Kingdom, Ireland, Germany, Switzerland, Austria and of course the United States.
US Cordset Manufacturing provides power-supply products to various categories of customers from domestic to industrial. Our line of products include wiring harnesses, Coiled cords, extension cords, processed wires, high voltage twist lock cords, and more. Whether your requested electrical configuration is simple or intricate, our expert staff is ready to help.

Our plug adapters are guaranteed to bring you a lifetime of value. Our staff is committed to bringing you only the most reliable products that are available. We will find solutions for your cord needs regardless of how difficult the job may be.

At Americord, we dedicate ourselves to delivering high-quality power cords and custom wiring solutions that meet the demands of diverse industries. We design and manufacture durable cords that are tailored for performance, safety, and reliability, serving applications ranging from consumer electronics and industrial machinery to specialized equipment requiring precise electrical connectivity.
At Cord-Sets, we dedicate ourselves to delivering high-quality power cord solutions that meet the needs of industries across the globe. We specialize in designing and manufacturing power cords, cord sets, and related components that are engineered for durability, safety, and reliable performance.

More Extension Cord Manufacturers
Extension Cords: Types, Applications, Safety, and Buying Guide
Extension cords are indispensable electrical accessories that enable the flexible and safe transmission of power from a fixed outlet to a wide range of electrical appliances and devices. Available in a variety of designs, extension cords are engineered to support different electrical loads, environments, and user requirements. Whether you're searching for a heavy-duty extension cord for construction, a weather-resistant outdoor extension cord for landscaping, or a compact indoor cord for household electronics, understanding the types, features, and best practices is crucial for selecting the right product.
What Is an Extension Cord?
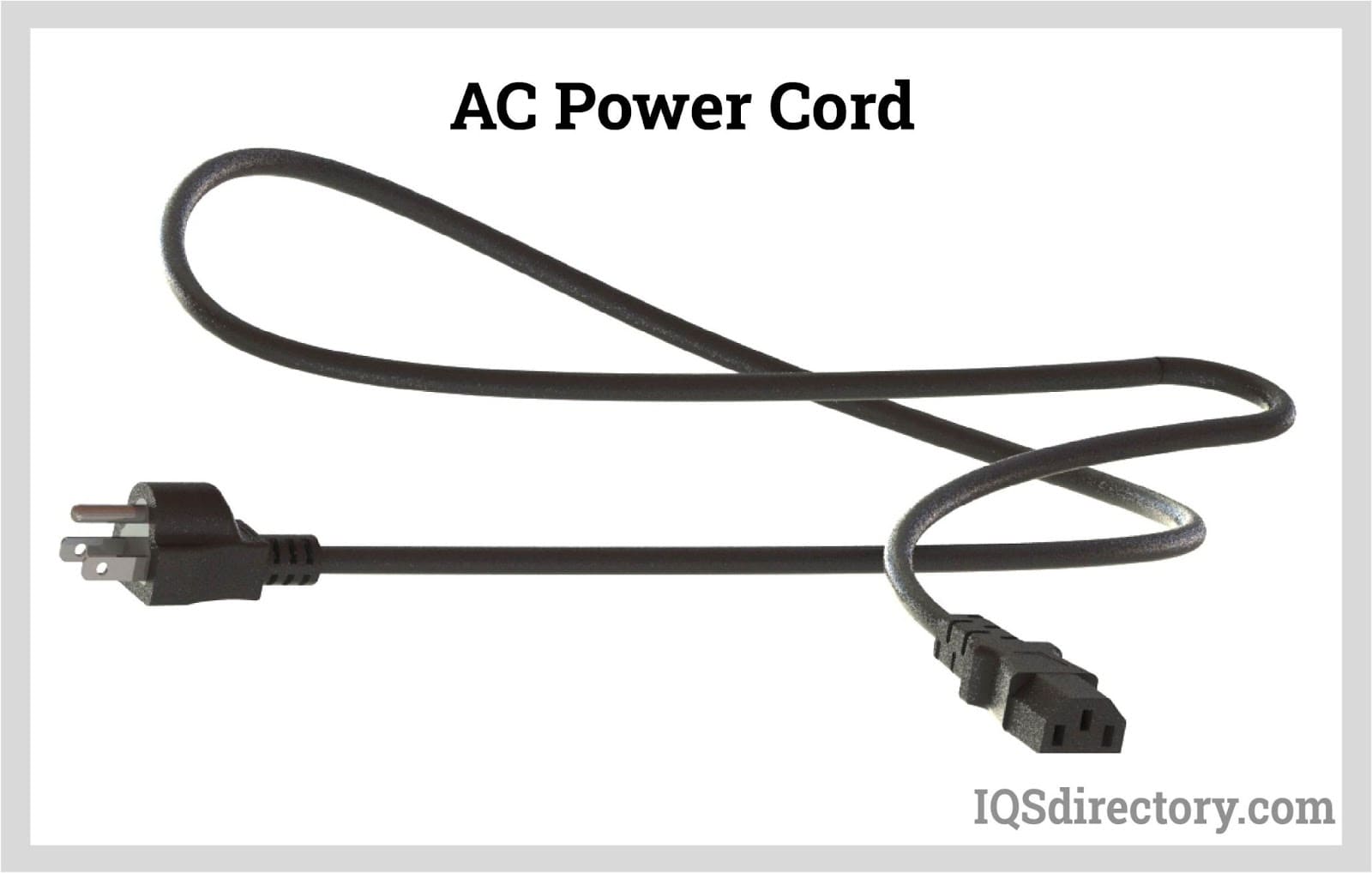
An extension cord is a flexible, insulated length of electrical cable featuring a plug (male connector) on one end and a socket (female connector) on the other. Its primary function is to extend the reach of a power source, enabling the connection of electrical devices that are located far from electrical outlets. The core components typically include copper conducting wires of varying gauges, protected by a durable rubber or thermoplastic jacket designed to insulate and safeguard the conductors from environmental hazards and physical damage.
Extension cords are also referred to as power extension cords, power strips (when featuring multiple outlets), or temporary power cables. They are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings due to their versatility and convenience.
Types of Extension Cords: Features and Applications
Extension cords vary greatly in construction, capacity, length, and intended use. The following are the most common types of extension cords available on the market:
- Light-Duty Extension Cords: Designed for indoor use with low-wattage appliances such as lamps, clocks, and small electronics. These cords typically have a thinner wire gauge (16 AWG or higher), limited amperage, and are not suitable for high-power equipment.
- Medium-Duty Extension Cords: Suitable for office equipment, computers, televisions, and kitchen appliances. These cords generally use a 14 AWG wire and offer a balance between flexibility and current-carrying capacity.
- Heavy-Duty Extension Cords: Built for power tools, air conditioners, and other demanding devices. Heavy-duty cords usually feature 12 AWG or lower gauge wires, thicker insulation, and may be rated for outdoor or industrial use.
- Outdoor Extension Cords: Equipped with weather-resistant and UV-protected jackets, these extension cords are ideal for landscaping, holiday lighting, and construction sites. They are often colored bright orange or yellow for visibility and safety.
- Specialty Extension Cords: These include locking extension cords for secure connections, GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) cords for wet environments, and retractable or coiled cords for easy storage and transport.
Common Applications for Extension Cords
Extension cords serve a multitude of applications, including:
- Providing temporary power to outdoor equipment, garden tools, and holiday decorations
- Powering computers, monitors, printers, and other office electronics
- Supplying electricity to power tools and machinery on construction sites
- Enabling flexible layout of home entertainment systems and audio/visual equipment
- Facilitating trade shows, events, and temporary workspaces where outlets are limited
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Looking for an extension cord for a unique application? Consider these common industry scenarios:
- Manufacturing and Warehousing: Powering conveyor belts, industrial fans, and portable machinery.
- Healthcare Facilities: Supplying electricity to medical devices or mobile diagnostic equipment.
- Hospitality and Events: Supporting temporary lighting, audiovisual setups, and catering equipment.
- Film and Broadcasting: Extending power to cameras, lighting rigs, and production trailers.
Understanding Extension Cord Ratings: Gauge, Length, and Capacity
Choosing the right extension cord requires careful consideration of technical specifications that impact both safety and performance. The most critical factors are:
- Wire Gauge (AWG): The American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard measures the thickness of the conducting wire. Lower numbers (e.g., 10 AWG, 12 AWG) indicate thicker wires capable of carrying more current. Using the correct gauge is essential to prevent overheating and voltage drop.
- Length: The total length of the cord affects its ability to transmit power efficiently. Longer cords experience greater resistance and voltage drop, which can impact the performance of connected devices. Always use the shortest cord possible for your needs.
- Amperage and Wattage Ratings: Each extension cord is rated for a maximum current (amps) and power (watts). Exceeding these ratings can lead to overheating, fire hazards, or equipment damage.
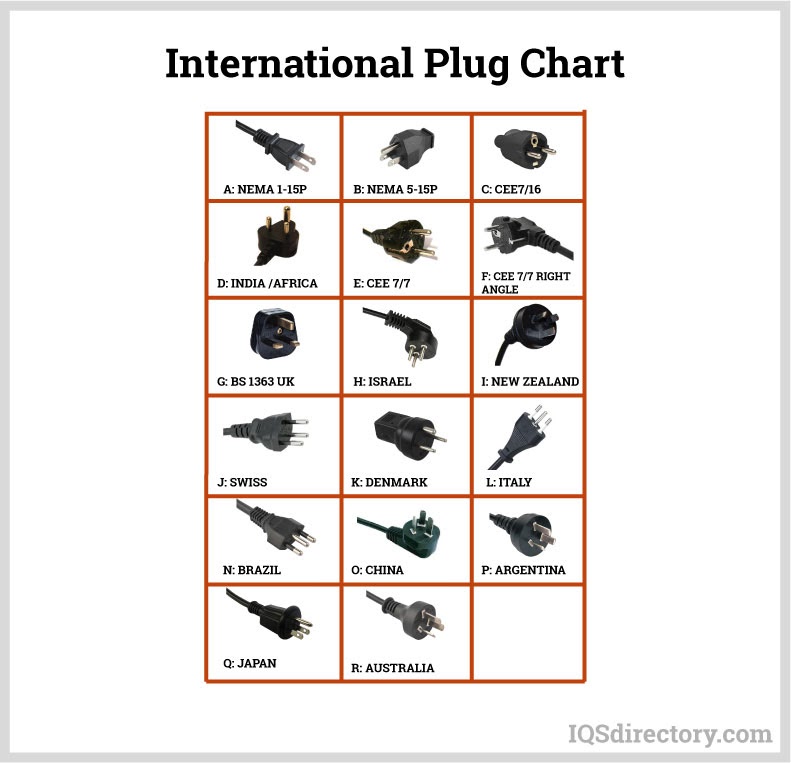
- Voltage Rating: Ensure the cord's voltage rating matches or exceeds the supply voltage in your region (e.g., 120V in North America, 220-240V in many other countries).
Quick Reference Table: Extension Cord Selection
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Maximum Amps | Recommended Maximum Length | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 10 | 50 ft (15 m) | Lamps, phones, light appliances |
| 14 | 15 | 100 ft (30 m) | TVs, computers, power tools |
| 12 | 20 | 100 ft (30 m) | Air conditioners, industrial tools |
| 10 | 30 | 150 ft (45 m) | Welders, large appliances |
Key Components and Construction of Extension Cords
The essential parts of an extension cord include:
- Conducting Wire: Usually made of copper for superior conductivity and durability. Some budget models may use aluminum, but copper is the industry standard for safety and efficiency.
- Insulation and Jacket: The inner insulation separates wires and prevents short circuits, while the outer jacket (rubber, thermoplastic, or vinyl) protects against abrasion, moisture, sunlight, and temperature extremes.
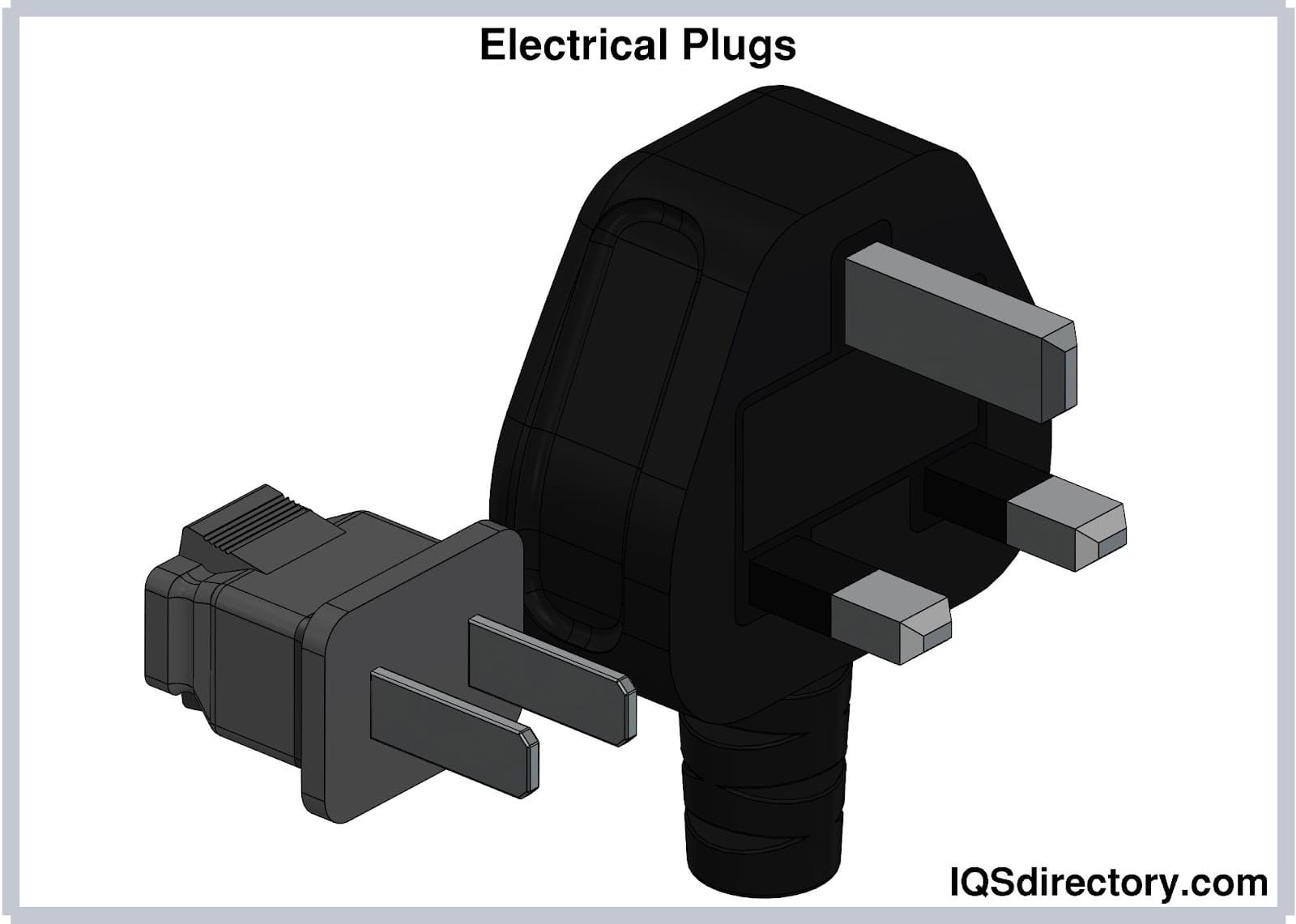
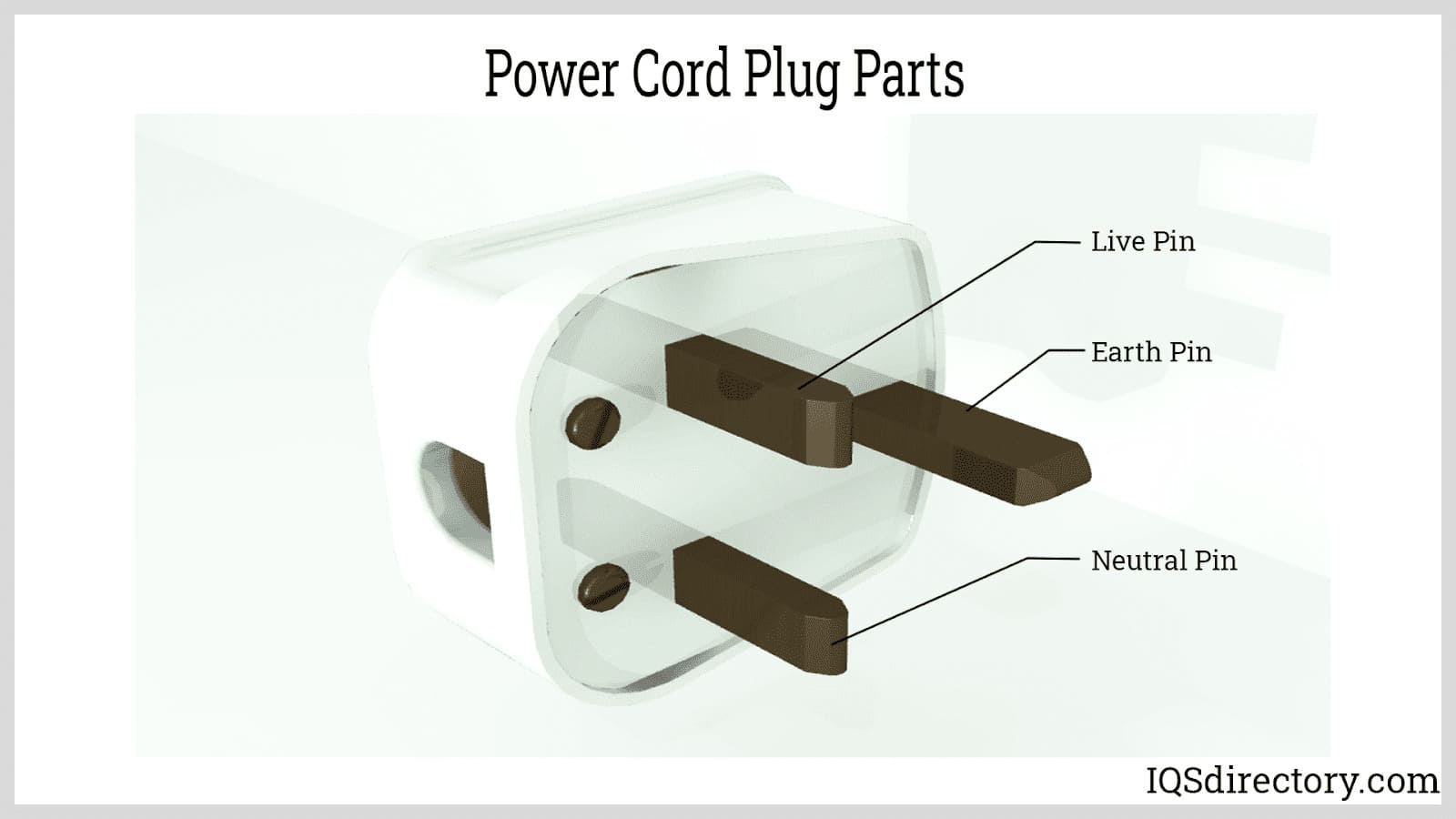
- Plug (Male Connector): The pronged end that fits into the wall socket or electrical receptacle. High-quality plugs ensure a secure, low-resistance connection for optimal energy transfer.
- Socket (Female Connector): The outlet end into which the appliance or device is plugged.
- Ground Pin: Many cords include a third (ground) pin to enhance safety and limit electrical shock risk.
How Does an Extension Cord Work?
Extension cords function by safely channeling electrical voltage from a wall outlet through the conducting wires to the connected device. The efficiency and safety of the transfer depend on the cord's design, including the quality of the connectors, the tightness of the plug-socket fit, and the gauge of the conducting wire.
Extension Cord Safety: Risks, Standards, and Best Practices
Extension cords are designed for temporary use and should not be relied upon as permanent wiring solutions. Improper use can result in electric shock, fire hazards, equipment damage, and even personal injury or death. To ensure safe operation, always follow these guidelines:
- Never exceed the rated amperage or wattage of the cord.
- Do not daisy-chain (connect multiple) extension cords together.
- Avoid using extension cords in wet or damp locations unless they are specifically rated for outdoor or GFCI use.
- Regularly inspect cords for damage, frayed insulation, or exposed wires, and replace immediately if any issues are found.
- Do not run cords under carpets, through walls, or in areas where they may be pinched or crushed.
- Store extension cords properly to prevent kinks or tangles that can damage the internal wires.
Extension Cord Safety Features
Modern extension cords often include built-in safety features, such as:
- Polarized Plugs and Sockets: Designed to connect to a ground wire and minimize shock hazards.
- Circuit Breakers and Fuses: Protect against power surges and overheating by interrupting the current flow if dangerous conditions are detected.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI): Essential for outdoor and wet-location cords to reduce the risk of electric shock.
- Child Safety Covers: Help prevent accidental contact with live parts.
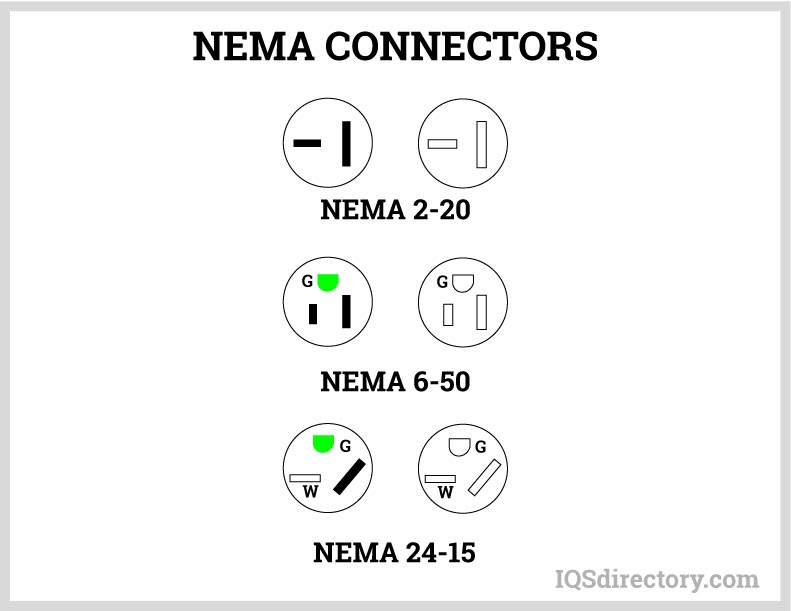
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) establishes standards for extension cord manufacturing and performance in North America, ensuring that cords meet strict safety, reliability, and quality requirements. When purchasing, look for cords labeled with a UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or ETL (Intertek) certification mark for added assurance.
How to Choose the Best Extension Cord: Buying Guide
When researching or shopping for the best extension cord for your needs, consider the following:
- Intended Application: Will you use the cord indoors or outdoors? For household electronics, power tools, or industrial equipment?
- Required Length: Measure the distance from the power source to your device, and select the shortest cord that will reach safely.
- Wire Gauge: Match the AWG rating to the power requirements of your equipment. Heavier loads require lower-gauge (thicker) wires.
- Safety Ratings and Certifications: Look for UL, ETL, or CSA certification, and ensure compliance with local electrical codes.
- Number of Outlets: Some extension cords feature multiple outlets, surge protection, or USB charging ports for added convenience.
- Special Features: Weather resistance, retractable design, lighted ends, locking connectors, or GFCI protection may be beneficial for specific use cases.
Frequently Asked Questions: Extension Cords
- What size extension cord do I need for my power tool?
Use a heavy-duty cord (12 AWG or lower) for power tools, especially if the cord is longer than 50 feet. - Can I use an indoor extension cord outdoors?
No, always use cords specifically rated for outdoor use to ensure safety and compliance. - What is the maximum safe length for an extension cord?
This varies by gauge and amperage, but longer cords increase resistance and voltage drop. Refer to the selection table above for guidelines. - How do I know if my extension cord is overloaded?
If the cord feels warm or hot, or if connected devices operate erratically, unplug immediately and use a higher-rated cord. - Are extension cords safe for permanent use?
No, extension cords are intended for temporary applications only. For permanent wiring, consult a licensed electrician. - What is a polarized plug?
A polarized plug has one prong wider than the other, ensuring the cord can only be plugged in one way for safety.
How to Use Extension Cords Safely: Step-by-Step
- Check the cord for damage before each use.
- Plug the male end into a grounded wall outlet.
- Connect the female socket to your device or appliance.
- Ensure the cord is fully uncoiled to prevent overheating.
- Never plug one extension cord into another ("daisy-chaining").
- After use, unplug the cord from the outlet and store properly.
Troubleshooting Common Extension Cord Problems
- Extension cord won't power device: Check both the outlet and the cord for faults, damage, or tripped breakers.
- Plug feels loose in outlet: Use a different outlet or replace worn plugs for a tighter, safer fit.
- Cord gets warm or hot: This indicates overloading or poor connections. Unplug and use a heavier-duty cord.
- Visible damage to jacket or insulation: Discard and replace the cord immediately.
Where to Buy Extension Cords: Sourcing and Supplier Selection
Extension cords can be purchased through a wide range of channels, including hardware stores, electrical supply distributors, online marketplaces, and specialty manufacturers. When sourcing extension cords for commercial or industrial purposes, consider working directly with a reputable extension cord manufacturer or distributor to ensure product quality, compliance, and bulk pricing.
Top factors to consider when choosing a supplier:
- Product certifications and warranty policies
- Customization options (length, color, plug/socket type)
- Availability of specialty cords (locking, GFCI, retractable, etc.)
- Support for large or recurring orders
- Technical support and after-sales service
Extension Cords and Regulatory Compliance
In North America, extension cords and related electrical products must comply with standards set by organizations such as NEMA, UL, ETL, and CSA. Compliance ensures that cords meet minimum safety, performance, and labeling requirements. When purchasing extension cords for commercial, industrial, or export use, always verify that the product meets local and international standards.
Did you know? Extension cords sold in the United States must feature a permanent label indicating the gauge, voltage, amperage, and maximum wattage. This helps users select the correct cord and prevents unsafe usage.
Advanced Considerations: Extension Cord Features, Customization, and Emerging Trends
As technology evolves, so do the requirements and offerings of extension cords. In addition to the core considerations above, buyers and specifiers should be aware of advanced features, customization options, and the latest trends in power extension technology:
- Surge Protection: Many modern extension cords and power strips offer built-in surge protection to safeguard sensitive electronics against voltage spikes caused by lightning or power surges. For computers, AV equipment, and home offices, surge-protected extension cords are highly recommended.
- Smart Extension Cords: Smart power cords integrate with home automation systems, allowing users to remotely control outlets, monitor energy usage, and set timers via smartphone apps or voice assistants. If you're upgrading your smart home or business, consider extension cords with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity.
- Retractable and Reel Extension Cords: Designed for workshops, garages, or industrial settings where cord management is critical, retractable reel extension cords reduce clutter, minimize tripping hazards, and extend cord life.
- Custom Extension Cords: For unique applications in manufacturing, medical, or industrial environments, custom extension cords can be specified with particular lengths, connectors, colored jackets, or additional weather/chemical resistance. Learn more about custom cable assemblies.
Are you seeking UL-listed, RoHS-compliant, or custom-designed extension cords? Request a quote from a specialty manufacturer or contact our team for expert guidance.
Environmental and Energy Efficiency Considerations
Extension cords play a role in overall energy efficiency and workplace safety. Choosing the correct gauge and length minimizes power loss due to resistance, helping to reduce wasted energy. Additionally, some manufacturers now offer extension cords made with eco-friendly materials, recyclable packaging, and lower-impact manufacturing processes. Look for "green" or energy-efficient extension cord options if sustainability is a priority for your project or organization.
- Tip: Always unplug extension cords when not in use to eliminate phantom loads and reduce fire risk.
- Question: Are there energy-saving extension cords or power strips for your application? Explore our resource library.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Extension Cord for Your Needs
Extension cords are vital components in modern electrical systems, bridging the gap between fixed outlets and mobile devices. By understanding extension cord types, ratings, and safety requirements, you can confidently select the best extension cord for your application—whether you need a heavy-duty industrial solution or a compact, flexible cord for home use. Always prioritize safety, follow manufacturer guidelines, and invest in certified, high-quality products to ensure reliable, long-lasting performance.
Ready to find the perfect extension cord?
- Browse our directory of electrical plug and extension cord manufacturers
- Request a quote for custom extension cord solutions
- Learn more about locking power cords and specialty options
Related Resources and Further Reading
Still have questions?
Contact us or ask about extension cord solutions for your specific application. Our experts are here to help you choose the safest, most reliable extension cord for your needs.
Search and Decision Prompts: Find the Right Extension Cord for Your Application
- What is the best extension cord for outdoor use in wet environments?
- Which extension cord should I use for high-powered tools on a construction site?
- How do I select a surge-protected extension cord for sensitive electronics?
- Where can I order custom-length extension cords with specific connectors?
- What are the safest extension cords for use in healthcare or medical settings?
- How do I compare extension cord gauges and maximum load capacities?
- Are there certified extension cords for international (220V/240V) applications?
- What features should I look for in an energy-efficient or eco-friendly extension cord?
Glossary: Key Extension Cord Terminology
- AWG (American Wire Gauge): Standard system for denoting wire diameter and current capacity.
- GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter): A safety device that protects against electrical shock in wet environments.
- NEMA: National Electrical Manufacturers Association, which sets industry standards for electrical products in North America.
- UL/ETL/CSA: Leading safety certification organizations for electrical products in the U.S., Canada, and worldwide.
- Voltage Drop: The reduction in voltage as electric current moves through a wire, especially significant in long extension cords.
- Polarized Plug: Plug with prongs of different widths to ensure safe and correct insertion.
- Surge Protector: Device or feature in some extension cords that absorbs excess voltage and protects devices from spikes.
Extension Cord Buying Checklist
- Identify your application and environment (indoor, outdoor, industrial, commercial, residential).
- Calculate the total wattage and amperage of devices to be powered.
- Choose the correct cord length—avoid excessive slack or insufficient reach.
- Select the proper wire gauge for your load and length requirements.
- Look for safety certifications (UL, ETL, CSA) and compliance with local codes.
- Consider advanced features (surge protection, GFCI, locking connectors) as needed.
- Inspect for build quality, including plug and socket design, jacket durability, and strain relief.
- Ask about warranty and technical support from your supplier.
Next Steps: Get Expert Advice or Request a Quote
Need help choosing an extension cord for your project, facility, or business? Contact our experts for personalized recommendations, technical specifications, or to request a quote for bulk or custom orders. Explore our knowledge base for detailed comparison guides, safety resources, and industry insights on extension cords, power strips, and related accessories.








 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services