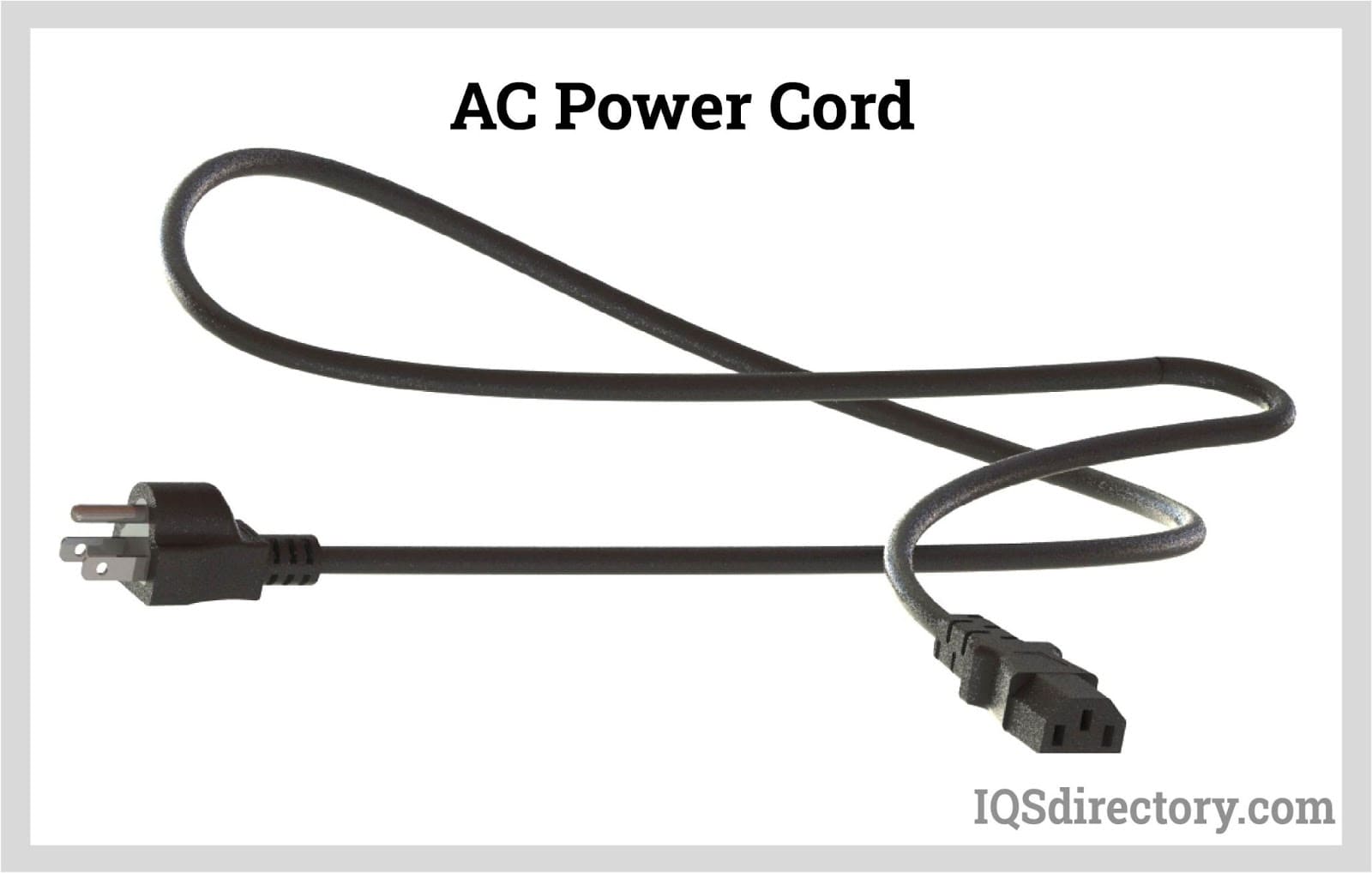
Cord sets are electrical cables used to connect an appliance or piece of equipment to a main power source. When connected, they provide electrical energy. They are also sometimes known as power cords, power supply cords, or electric cords. They are distinct in that they have connectors molded to their cords at each end, and they are detachable from both the power supply and the electrical equipment. Read More…
Our customers find we have the highest standards when it comes to quality, and delivery. Quail Electronics is a worldwide power cord supplier, offering power cords and various other products.
All of our power cords are tested and stand up to rigorous demands of everyday application. We serve a global market including the United Kingdom, Ireland, Germany, Switzerland, Austria and of course the United States.
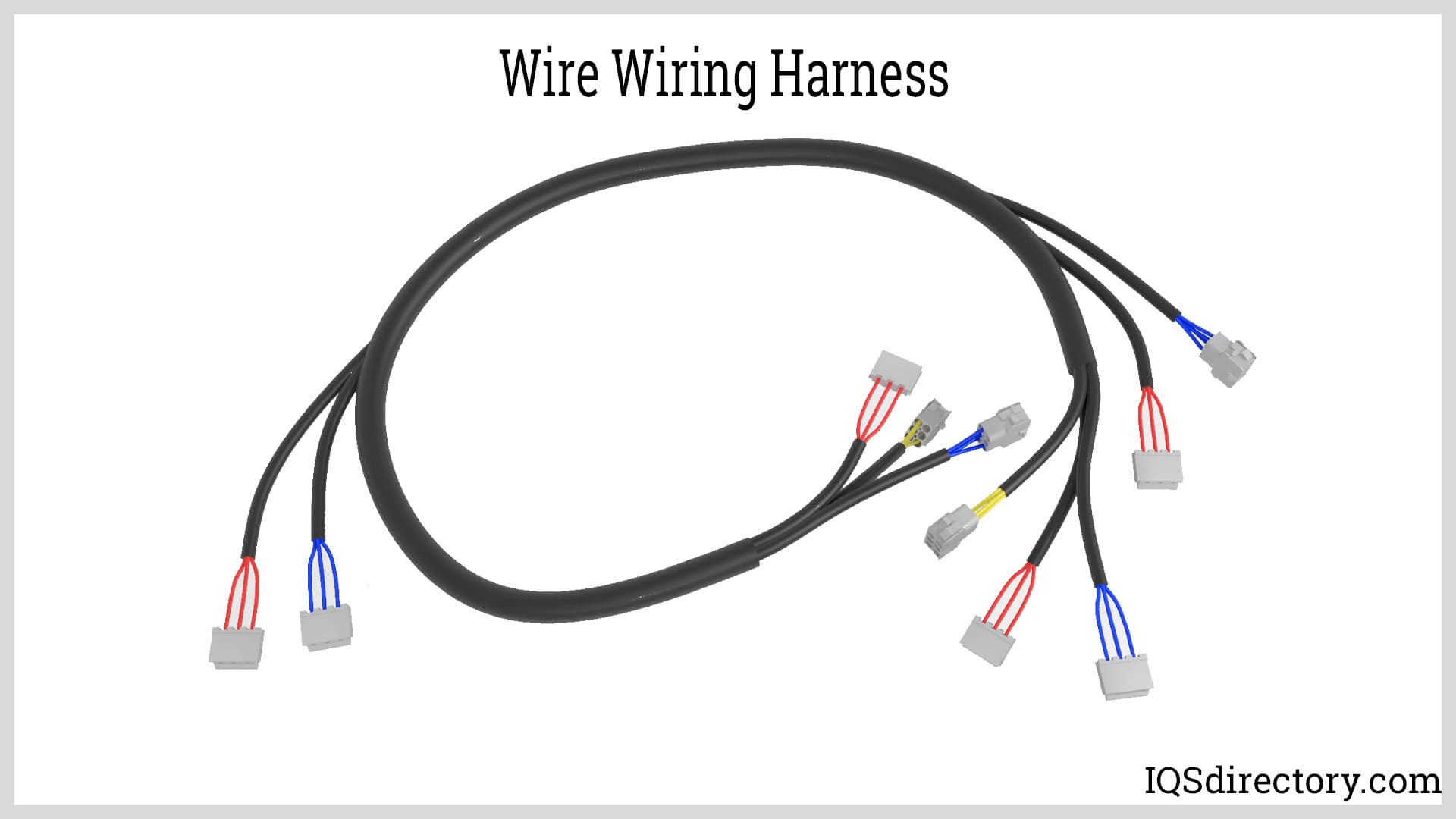
US Cordset Manufacturing provides power-supply products to various categories of customers from domestic to industrial. Our line of products include wiring harnesses, Coiled cords, extension cords, processed wires, high voltage twist lock cords, and more. Whether your requested electrical configuration is simple or intricate, our expert staff is ready to help.

Our plug adapters are guaranteed to bring you a lifetime of value. Our staff is committed to bringing you only the most reliable products that are available. We will find solutions for your cord needs regardless of how difficult the job may be.

At Americord, we dedicate ourselves to delivering high-quality power cords and custom wiring solutions that meet the demands of diverse industries. We design and manufacture durable cords that are tailored for performance, safety, and reliability, serving applications ranging from consumer electronics and industrial machinery to specialized equipment requiring precise electrical connectivity.
At Cord-Sets, we dedicate ourselves to delivering high-quality power cord solutions that meet the needs of industries across the globe. We specialize in designing and manufacturing power cords, cord sets, and related components that are engineered for durability, safety, and reliable performance.

More Power Cord Manufacturers
Cord sets—commonly referred to as power cords, power supply cords, electric cords, or line cords—are specialized electrical cables designed to connect appliances, equipment, and devices to a main power source. These essential components transmit electrical energy and feature molded connectors at each end, making them detachable from both the power supply and the equipment for maximum flexibility. Their design and construction play a vital role in electrical safety, energy efficiency, and equipment performance across a variety of industries and applications.
Applications of Cord Sets
Power cords are indispensable across countless industries, acting as the lifelines that deliver electrical power to machinery, systems, and devices. Also known as power cables or line cords, these versatile cables ensure uninterrupted power delivery, even in the most demanding environments. In this guide, we’ll explore the broad spectrum of industrial applications for power cords, highlight their key benefits, and discuss the critical requirements they fulfill across different sectors.
What Are Power Cords in Industrial Contexts?
In industrial settings, power cords are engineered as heavy-duty cables designed to safely transmit electricity from a power source (such as wall outlets, generators, or power distribution units) to equipment, machinery, or systems. These cords are manufactured using robust insulation materials like rubber, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), thermoplastic elastomers, and even advanced compounds for specialized applications. The conductive core is typically copper or, less commonly, aluminum—both chosen for optimal electrical conductivity and minimal energy loss.
Industrial and commercial power cords frequently feature specialized connectors, including NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association), IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), or locking connectors, to guarantee secure, reliable, and safe electrical connections. Designed for high-voltage and high-current operation, these cords endure harsh environmental conditions such as abrasion, humidity, exposure to chemicals, and extreme temperatures, making them suitable for a wide range of challenging industrial settings.
Key Industrial Applications of Power Cords
Power cords play a crucial role in powering equipment, supporting automation, and maintaining operational continuity in various sectors. Here are some primary applications and their specific use cases:
- Manufacturing and Assembly Lines
- Machinery Power Supply: Connecting heavy machinery (CNC machines, lathes, presses, robotic arms) for continuous, automated operation.
- Conveyor Systems: Supplying electricity to conveyor belt motors for seamless material and product movement.
- Welding Equipment: Handling high current loads for industrial welding machines in automotive and metal fabrication shops.
- Benefits: Ensuring reliable, uninterrupted power to support production speed and minimize costly downtime.
- Construction and Heavy Industry
- Portable Tools and Equipment: Powering drills, saws, grinders, cranes, pumps, compressors, and other heavy-duty tools on job sites.
- Temporary Power Distribution: Connecting portable generators to temporary power systems for lighting, HVAC, and other systems during construction or events.
- Mining Operations: Powering drills, ventilation, and material handling equipment with abrasion-resistant, rugged cords.
- Benefits: Withstanding mechanical stress, dust, and moisture to ensure safe, consistent power delivery in rugged environments.
- Food and Beverage Processing
- Processing Equipment: Powering mixers, grinders, slicers, ovens, and packaging machines in food production lines.
- Refrigeration Systems: Running industrial refrigerators and freezers with heavy-duty cords for continuous cooling.
- Conveyor Systems: Driving conveyance for washing, cooking, and packaging food products.
- Benefits: Featuring food-grade, moisture-resistant insulation for safety and hygiene, compliant with FDA and USDA standards.
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Drilling Rigs: Supplying electricity to drilling equipment and pumps, with cords designed for oil and chemical resistance.
- Refinery Equipment: Powering motors, pumps, and heaters used in refining processes.
- Pipeline Monitoring: Delivering power to control and monitoring systems along pipelines for operational safety.
- Benefits: Engineered for flame-retardance, corrosion resistance, and safety in hazardous environments.
- Automotive Manufacturing
- Robotic Assembly Lines: Powering robotic arms for welding, painting, and assembling automotive components.
- Testing Equipment: Connecting diagnostic and emissions testing devices in quality control processes.
- Charging Stations: Supplying power to EV charging and battery testing systems.
- Benefits: Ensuring consistent power to high-precision, automated production equipment.
- Pharmaceutical and Medical Manufacturing
- Production Equipment: Supplying mixers, granulators, tablet presses, and packaging machines in cleanroom environments.
- Cleanroom Systems: Powering HVAC and air filtration with non-shedding, contamination-resistant cords.
- Laboratory Equipment: Connecting analytical instruments, incubators, and centrifuges in research and QC labs.
- Benefits: Meeting strict hygiene standards and chemical resistance for pharmaceutical safety and compliance.
- Data Centers and IT Infrastructure
- Server Racks: Connecting servers, storage, and networking equipment to power distribution units (PDUs).
- Cooling Systems: Powering fans, chillers, and climate control to maintain optimal server temperatures.
- Backup Power Systems: Linking UPS systems and generators to critical IT hardware for disaster recovery.
- Benefits: High-reliability cords with locking connectors for uptime and data integrity.
- Aerospace and Defense
- Aircraft Manufacturing: Powering assembly tools and testing equipment for aircraft production.
- Ground Support Equipment: Providing electricity to airfield lighting, tugs, and maintenance tools.
- Military Field Operations: Connecting communication, radar, and support systems with MIL-SPEC-compliant cords.
- Benefits: Flexible, rugged cords engineered for extreme reliability and environmental resistance.
- Energy and Power Generation
- Generator Connections: Linking portable and stationary generators to equipment during outages or maintenance.
- Control Systems: Powering control panels and monitoring systems in power plants.
- Renewable Energy: Connecting solar inverters, wind turbines, and monitoring devices with weather-resistant cords.
- Benefits: Reliable power distribution and safety in high-voltage, high-demand environments.
Thinking About Power Cord Applications?
- What type of environment will your power cord be used in—indoor, outdoor, industrial, or commercial?
- Do you need cords with specialized insulation for food-grade, medical, or hazardous locations?
- Are you searching for extension cords, AC power cords, or custom power cables?
Benefits of Power Cords in Industrial Applications
Power cords offer several significant benefits for industrial and commercial users:
- Reliability: Engineered to deliver steady, uninterrupted power even under demanding or continuous use.
- Durability: Built to withstand abrasion, heat, chemicals, and moisture for long-term performance.
- Safety: Incorporate features such as flame-retardant insulation, locking connectors, and grounding options to minimize electrical risks.
- Versatility: Available in various lengths, gauges, and connector types to suit diverse applications and power requirements.
- Ease of Use: Designed for straightforward installation, quick replacement, and minimal maintenance downtime.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Industrial Power Cords
Choosing the right power cord for your application is essential for safety, efficiency, and compliance. Key factors include:
- Voltage and Current Rating: Select cords rated for your equipment’s voltage and current (e.g., 120V, 240V, 480V, 15A, 30A).
- Environmental Conditions: Choose insulation and jacketing materials to resist oil, UV rays, chemicals, or water as required.
- Connector Type: Match your equipment’s requirements with the proper NEMA, IEC, or specialty connector.
- Length and Flexibility: Ensure adequate length and flexibility for your installation, particularly where frequent movement or bending is involved.
- Compliance: Verify cords meet standards such as UL, CSA, RoHS, or IEC and adhere to local and international safety regulations.
Questions to Guide Your Power Cord Selection
- What are the voltage and current requirements for your application?
- Will the power cord be exposed to chemicals, water, or abrasion?
- Do you need a standard or custom connector type?
- Is certification (UL, CSA, RoHS, IEC) required for your application?
The History of Cord Sets
The evolution of the power cord traces back to the earliest days of electrical power distribution. In 1882, Thomas Edison established the first commercial power distribution system in New York City, inspired by a similar setup he pioneered in London. These early systems, the forerunners of modern cord sets, transmitted direct current (DC) using copper rods insulated with jute and encased in rigid, asphalt-filled pipes.
By the late 1880s, the introduction of vulcanized rubber as an insulator—an innovation patented by Charles Goodyear—enabled safer and more durable cables, exemplified by the 1897 Niagara Falls project that used rubber-insulated wires for high-voltage circuits. The 20th century saw further advancements, including polyethylene and synthetic rubber insulation by World War II.
Homes and businesses in America experienced significant improvements in cord safety and design. Early power cords were bare or cloth-covered wires, but by the 1930s, insulated rubber or asphalt-saturated cloth cord sets became standard. The 1906 development of armored cable (“Bx”) and later, two-wire PVC-insulated “Romex” cables in the 1950s, marked leaps in safety and convenience. The migration from aluminum wiring in the 1960s–1970s and the elimination of asbestos insulation further improved safety. Today, three-wire PVC-insulated cables and USB adaptors offer safe, efficient power for residential and commercial use.
Design of Power Cords
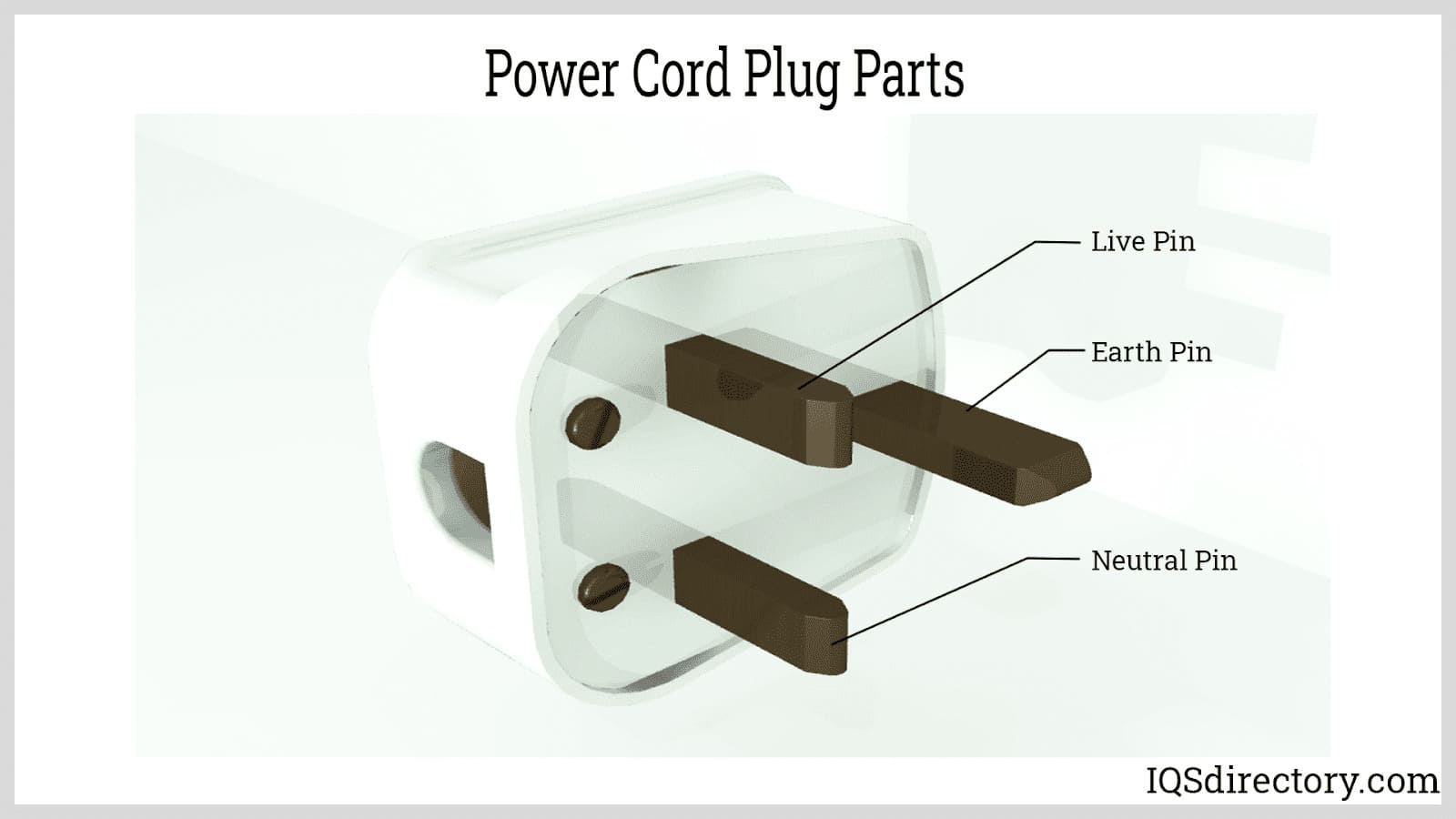
A standard power cord set consists of a flexible cable with electrical connectors—one male and one female—at each end, encased in insulating and protective materials. The cord contains highly conductive copper wire, a choice that has remained consistent due to its low resistance and reliability.
Insulative materials are selected for their temperature ratings and electrical properties, with common options including PVC, semi-rigid PVC, plenum PVC, polyethylene, polypropylene, polyurethane, chlorinated polyethylene (CPE), nylon, thermoplastic rubber (TPR), silicone, fiberglass, ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), SBR, EPDM, and TPE. For jacketing, TPE, PVC, and neoprene are popular due to their oil, heat, and moisture resistance.
Construction must comply with standards for voltage, current, wire gauge (measured by American Wire Gauge, AWG), cable length, temperature, and connector type. Manufacturers can customize cords for specific applications, choosing shape (flat or round), gauge (AWG), length, color, and even plug configurations such as rotating, snap-on, screw-on, or locking types. Special-purpose jackets—like waterproof or electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding—are available for demanding environments.
Looking for Custom Power Cord Design?
- Do you require custom wire gauge, length, or connector types for your application?
- Is environmental resistance (oil, water, UV) or EMI shielding critical for your equipment?
- Would colored or labeled cord sets improve your facility’s organization and safety?
Features of Cord Sets
Cord sets are designed to transfer either direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC), with AC being the prevalent choice for modern electrical systems due to its efficiency and suitability for long-distance transmission. AC power cords are widely used in both residential and industrial settings.
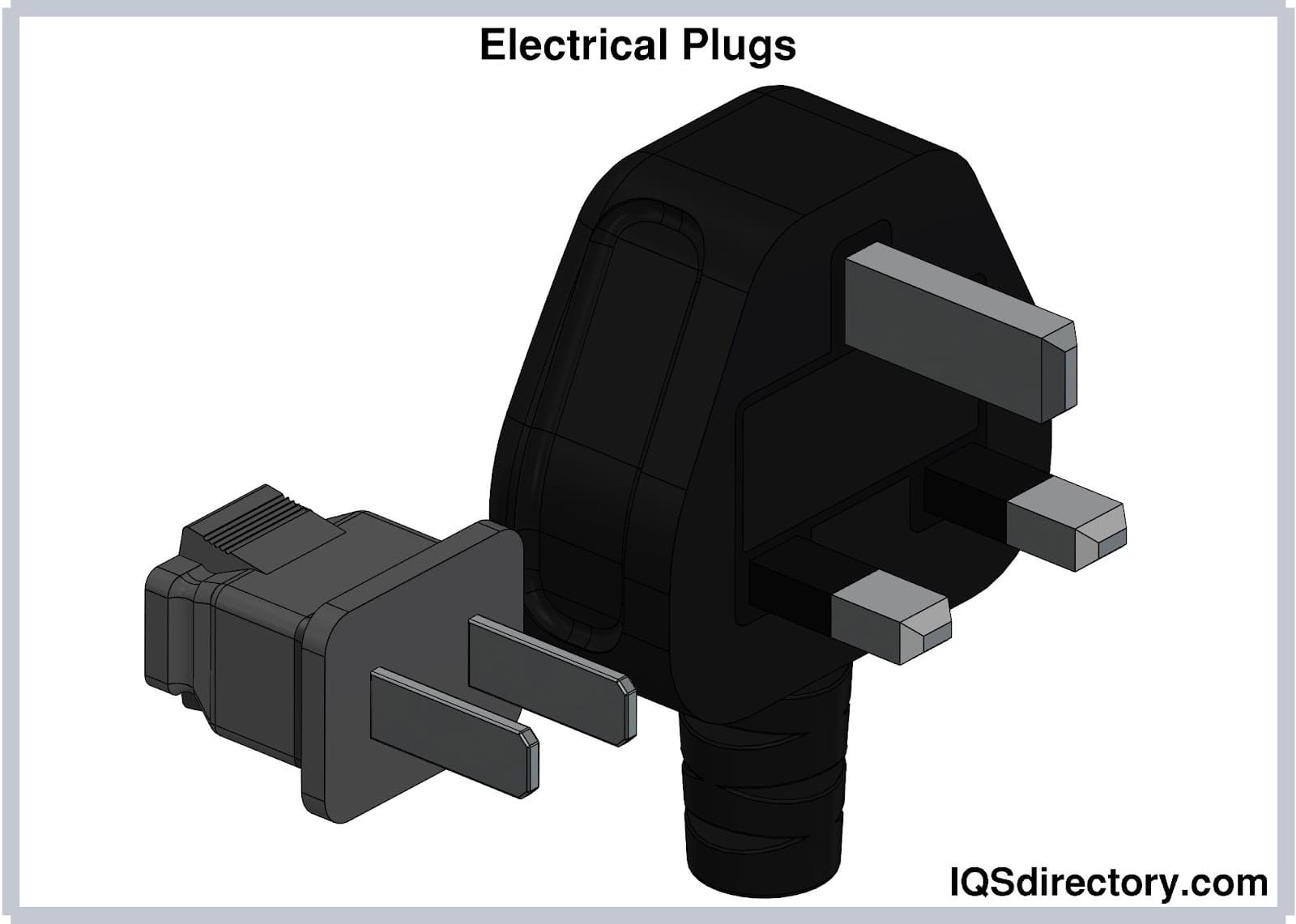
Standard cord sets feature detachable connections at both ends, enabling quick disconnection from the device and the power source. The female connector attaches to the equipment, while the male plug connects to the power outlet, ensuring secure and safe connections.
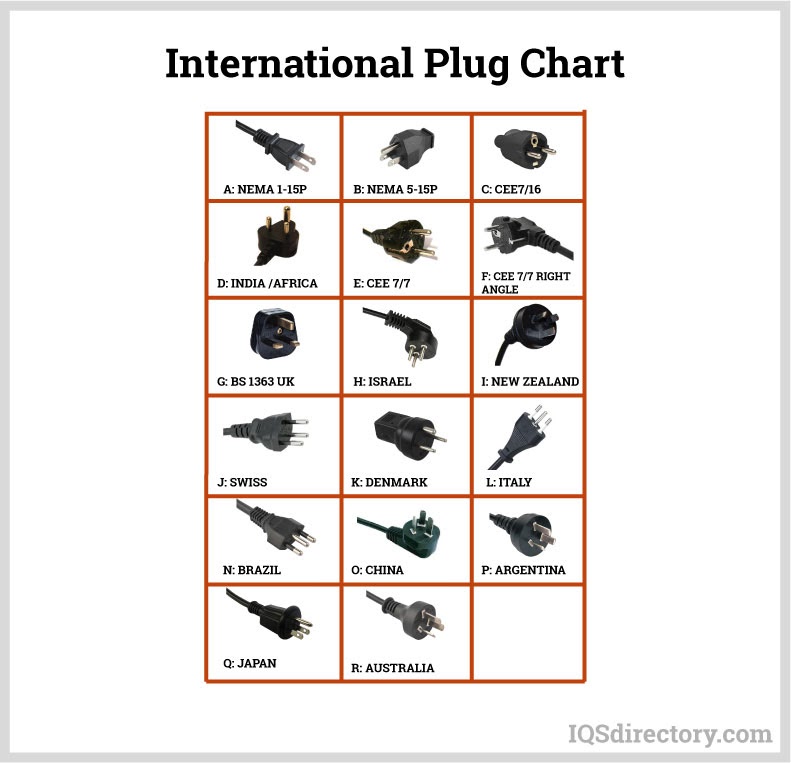
Depending on the application, cords may be permanently attached to a plug or require a power adaptor (AC adaptor or outlet adaptor). In North America, Type A (two-prong) and Type B (three-prong, grounded) plugs are common. Internationally, plug and socket types vary, requiring region-specific solutions.
Advanced power adapters convert AC to DC voltage and may feature surge protection, EMI filters, voltage monitoring, and various connector styles such as North American, International, Universal, IEC, and USB.
Types of Cord Sets
Specialized cord sets address the needs of various environments and industries:
- Business Machine Cords: Built for computers, servers, and office electronics, ensuring compatibility and safe operation.
- Heavy-Duty Cords: Designed for rugged industrial and commercial use, featuring robust insulation, strain relief, and non-slip grips.
- Hospital Plugs: Engineered to meet stringent medical standards, with conductors welded or soldered to solid brass for maximum reliability.
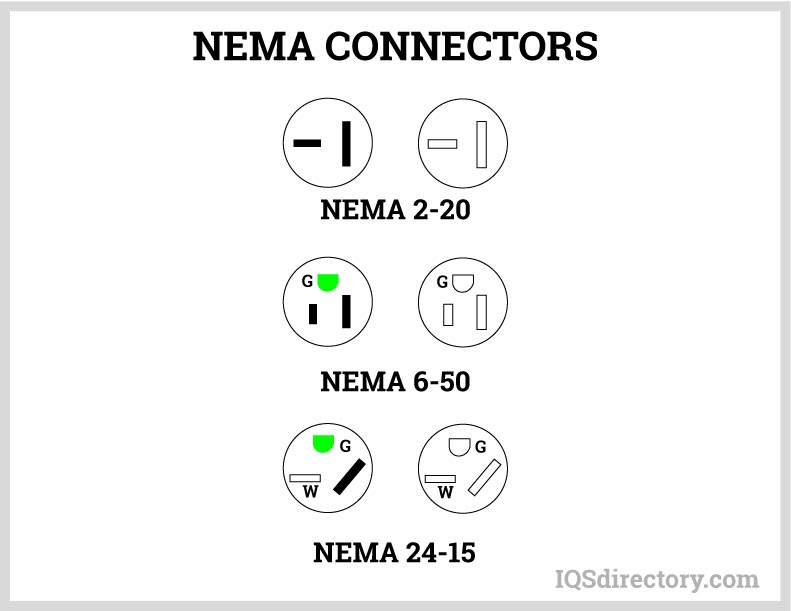
- NEMA Power Cords: Compliant with NEMA standards for voltage capacity and configuration, ensuring safe, standardized connections in North America.
- Right Angle Power Cords: Allow connections in tight spaces, reducing cord stress and increasing longevity.
- Power Strips: Provide multiple outlets from a single source, ideal for offices, workshops, and entertainment systems. Often feature surge protection and circuit breakers for safety.
- Extension Cords: Extend the reach of power cords for temporary or permanent installations in homes, offices, and worksites.
Common Search Questions About Cord Types
- What’s the difference between a heavy-duty cord and a standard power cord?
- Which NEMA plug type is compatible with my equipment?
- Are right-angle cords better for tight installations?
- How do I choose the safest power strip for my workspace?
Advantages of Cord Sets
Cord sets provide a host of advantages for end-users and industries alike:
- Plug-and-Play Simplicity: Enables quick, tool-free installation and device replacement.
- Enhanced Safety: Features like grounding, double insulation, and robust connectors protect users and equipment.
- Standardization: Uniform plug types and voltage ratings simplify global compatibility and replacement.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Mass production and standard designs reduce costs compared to custom wiring solutions.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Available in a wide range of lengths, configurations, and ratings for diverse applications—from small gadgets to industrial machinery.
These advantages make cord sets crucial in sectors such as healthcare, IT, manufacturing, and consumer electronics—enabling everything from smartphone charging to powering factory robotics.
Cord Set Accessories
A range of accessories enhances the performance, safety, and versatility of cord sets:
- Adaptors: Bridge regional or device-specific plug standards, ideal for international travel or equipment compatibility.
- Fuses: Provide overcurrent protection, automatically disconnecting during overloads to prevent device damage.
- Insulating Tape and Shrink Tubing: Offer added insulation and environmental protection for exposed connections.
- High-Temperature Silica Tape: Shields cords in extreme heat environments such as automotive and industrial applications.
- Grip Seals: Prevent accidental disconnection and relieve strain at connection points.
- Cable Cutters and Wire Strippers: Ensure clean, precise wire preparation for optimal performance.
- Cable Sleeves: Prevent tangling and protect wires from abrasion or external damage.
- Pilot Lamps: Indicate power status or device function for added safety and monitoring.
- Leakage Current Detectors: Ensure safety by identifying unintended current flow, especially in medical or sensitive equipment.
Looking for Accessories or Upgrades?
- Do you need plug adaptors for international use?
- Is surge protection a priority for your application?
- Would cable sleeves or cord organizers improve your workspace safety?
Proper Care for Cord Sets
Proper maintenance and handling are crucial for extending the life, performance, and safety of cord sets:
- Handle cords gently—avoid sharp bends, kinks, or pulling which can damage internal wiring.
- Inspect regularly for wear, fraying, or insulation damage. Replace damaged cords immediately to prevent electrical hazards.
- Keep cords away from heat sources, sharp objects, and moisture to minimize deterioration.
- When unplugging, always grasp the plug, not the cord, to prevent connector damage.
- Clean with a dry or slightly damp cloth—never use harsh chemicals or submerge connectors.
- Store cords in cool, dry locations, coiled loosely to prevent kinks.
- Use cords rated for your application’s load and environment—outdoor-rated cords for exterior use, and shielded cords where EMI may be present.
- Unplug cords when not in use to conserve energy and reduce risk.
Maintenance Questions to Consider
- How often should you inspect your cords for wear or damage?
- What’s the best way to store extension cords to avoid kinks and tangles?
- Are you using outdoor-rated cords for exterior applications?
Standards for Cord Sets
Adherence to electrical standards ensures safety, compatibility, and quality:
- NEMA Standards: Define voltage capacities, plug designs, and receptacle configurations for North America, enhancing user safety and product consistency.
- American Wire Gauge (AWG): Specifies wire dimensions and voltage limits, critical for selecting the right cord gauge.
- International Standards: Countries use different voltages, plug shapes, and safety codes. International travelers or global businesses often require plug adapters or region-specific power cords.
- UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) collaborates with manufacturers to verify compliance for both domestic and international markets, ensuring environmental responsibility and safety.
Standards and Compliance FAQs
- Is your power cord certified for use in your country or region?
- Does your application require RoHS, UL, or CSA compliance?
- Are your cords properly rated for voltage and current?
How to Select a Power Cord Manufacturer
Selecting the right power cord manufacturer is pivotal for industries such as manufacturing, construction, food processing, IT, and data centers, where uninterrupted, safe power delivery is mission-critical. Reliable power cord manufacturers supply high-quality cords tailored to your application’s needs, adhering to safety standards and supporting operational efficiency. IQSDirectory.com, a premier industrial supplier platform, streamlines this process by connecting buyers with top North American power cord manufacturers and suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Power Cord Requirements
Identify the type of equipment, voltage/current ratings, environmental conditions, cord standards (NEMA, IEC), and length/gauge specifications your application demands. Use these criteria to focus your search on IQSDirectory.com.
Step 2: Navigate to the Power Cord Category on IQSDirectory.com
Visit IQSDirectory.com, search for “power cord manufacturers,” “custom power cords,” or related phrases, and filter by state or region if a local supplier is preferred for faster delivery and support.
Step 3: Explore Manufacturer Profiles and Previews
Use the patented preview feature to quickly assess offerings, and click through to detailed company profiles for contact information, product descriptions, videos, and customer reviews. Shortlist manufacturers specializing in your application or industry.
Step 4: Evaluate Manufacturer Experience and Expertise
Review company history, focus areas, and customer feedback. Prioritize manufacturers with a strong record in your industry and those offering custom solutions with specialized connectors, insulation, or branding.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Options
Use IQSDirectory.com’s RFQ tool to contact multiple suppliers, specifying your requirements for voltage, length, application, and certifications. Compare quotes on price, lead time, and value-added services.
Step 6: Verify Manufacturer Reputation and Support
Check for up-to-date company information, review the IQS Newsroom for current news, and contact manufacturers directly to evaluate support quality and responsiveness.
Step 7: Consider Geographic Proximity and Delivery Speed
Select local manufacturers if fast delivery or on-site support is crucial. Use location filters to find suppliers in states like California, North Carolina, or Wisconsin with wide product selections and competitive pricing.
Additional Tips for Using IQSDirectory.com
- Explore related categories for extension cords, cord sets, or power supply cords if your needs are specialized.
- Share company profiles and reviews with your team or stakeholders for collaborative decision-making.
- Provide feedback to IQSDirectory.com to help improve their supplier-matching services.
Why Use IQSDirectory.com?
- Targeted, industrial-specific search results for power cord and cable manufacturers.
- Comprehensive company profiles including reviews, videos, and product literature.
- Time-saving patented features such as instant website previews and multi-supplier RFQs.
- Geographic filtering to find local or regional suppliers for faster service and support.
Ready to Start Your Power Cord Supplier Search?
- What certifications and standards do you require for your project?
- Do you need custom labeling, packaging, or specialized cord features?
- Would a local supplier reduce your lead times and shipping costs?
For a broad selection of power cord products, detailed industry resources, and direct supplier connections, check out our Power Cords website.
Whether you’re sourcing UL-listed power cords for medical equipment, heavy-duty extension cords for construction, or custom NEMA cables for manufacturing, leveraging the right information and supplier network will ensure your power delivery is safe, reliable, and efficient.
What is a cord set or power cord?
A cord set, commonly called a power cord, power supply cord, electric cord, or line cord, is a specialized electrical cable designed to connect appliances and equipment to a main power source. It features molded connectors at each end, allowing it to be detachable for flexibility and safety in transmitting electrical energy.
What are the key applications of power cords in industry?
Industrial power cords are widely used to power machinery, portable tools, conveyor systems, welding equipment, food processing machines, refrigeration units, robotic assembly lines, laboratory devices, server racks, and more. They are essential for maintaining continuous operation and supporting automation in sectors including manufacturing, construction, food and beverage, oil and gas, automotive, pharmaceuticals, data centers, and defense.
Which factors should I consider when selecting an industrial power cord?
When choosing an industrial power cord, consider the voltage and current rating, environmental conditions (such as exposure to oil, chemicals, or water), connector type (e.g., NEMA, IEC), cord length and flexibility, and compliance with standards like UL, CSA, RoHS, or IEC. Proper selection ensures safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
What are the most common types of cord sets?
Common types of cord sets include business machine cords (for computers and electronics), heavy-duty cords (for industrial use), hospital plugs (for medical settings), NEMA power cords (North American standards), right angle power cords (for tight spaces), power strips, and extension cords for extending reach and flexibility.
What are key features and benefits of industrial power cords?
Industrial power cords offer reliability, durability, safety, versatility, and ease of use. They are engineered for steady power delivery, robust against abrasion, heat, chemicals, and moisture, and may include safety features like flame-retardant insulation, locking connectors, and grounding. Standardization and plug-and-play designs simplify installation and maintenance.
How should I properly maintain and care for power cords?
Handle cords gently, avoid sharp bends or pulling, and inspect regularly for damage. Keep cords away from heat, moisture, and sharp objects. Always unplug by gripping the plug, not the cord, and store cords loosely coiled in dry, cool places. Use cords rated for the specific application and unplug when not in use to extend life and maintain safety.
What certification standards should industrial power cords meet?
Industrial power cords should meet standards such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification, NEMA specifications (North American standards for plugs and receptacles), American Wire Gauge (AWG) for wire size, and, where applicable, international certifications like CSA, IEC, or RoHS for global compliance and safety.
What accessories can be used to enhance cord set performance and safety?
Cord set accessories include adaptors (for regional plugs), fuses (overcurrent protection), insulating tape, shrink tubing, high-temperature silica tape, grip seals, cable cutters, wire strippers, cable sleeves, pilot lamps, and leakage current detectors. These enhance safety, compatibility, protection, and performance for diverse applications.




 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services